3. slope of perpendicular lines
수직인 직선의 기울기
slope of
perpendicular lines
"수직인 두 직선의 기울기 곱은 -1"
" slopes of perpendicular lines are
negative reciprocals "
수직인 두 직선의
기울기를 서로 곱하면, 왜 항상 – 1 이 성립하는지에 대한
질문이 있어, 이에
대한 보충 설명을
하도록 합니다.
고등 수학의 이과
과정까지 공부를 한
학생이라면, 아래의 방법
등으로 간단하게 증명할
수 있습니다.
(a)
행렬을 이용한 90˚ 회전
변환 (rotation matrix)
(b)
삼각함수의 덧셈정리를 활용한 tan (α – β) = π / 2 (formula
for the difference of tangents)
(c)
벡터의 내적을 이용한A • B = |A| |B| cos θ = 0 (inner product of vectors)
그러나,
일반적인 중학생 또는
문과 고등학생의 수준에
맞도록, (1) 도형기하 (synthetic
geometry) 와
(2) 해석기하 (coordinate geometry) 의 2 가지
증명 방법만으로 설명하고자
합니다.
물론,
기하를 이용한 증명
과정의 설명이 더
복잡하고 지루할 수도
있습니다만, 좌표평면에서의 계산을
이용하는 해석기하의 방법은, 고등수학에서 배우는 내용이니까, 응용력의
향상을 위해서라도 철저하게
기본개념과 해결과정을 이해해
두기 바랍니다.
♧ ♧ ♧ ♧ ♧ ♧
스마트폰에서 수학 수식을 보시려면, 왼쪽 버튼을 누른 후
[데스크톱 보기] 를 설정하세요.
You can read math equations
by selecting [desktop view] on the mobile
[
A ] 도형 기하 (synthetic geometry) 의
방법
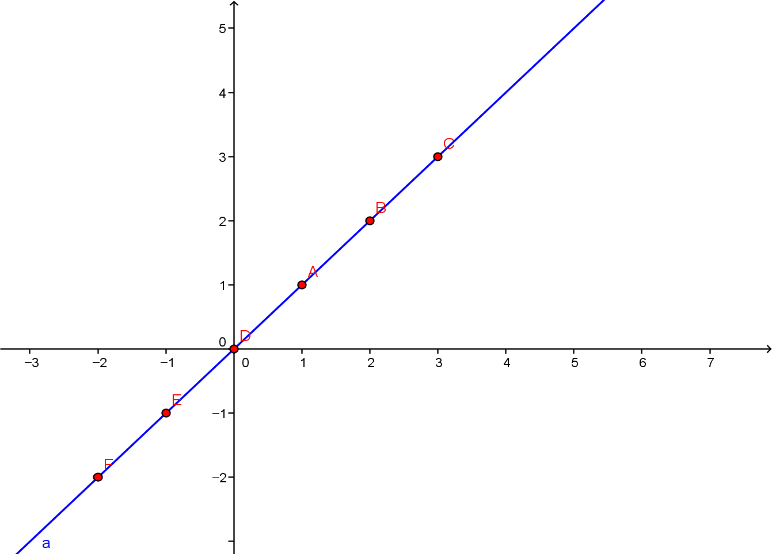
직선을 평행 이동시켜도
그 기울기는
변하지 않으니까, 원점을
지나면서 기울기가 서로
수직인 두 직선으로
예를 들어서, 두
기울기의 곱 = – 1 이라는 것을
증명하더라도, 일반성을 훼손하지
않겠지요?
Parallel shift doesn't change the slope of an original line and
accordingly, we're going to prove the fact that the product of slopes = – 1 with
two perpendicular lines that pass
through the origin (0, 0).
그러면,
아래의 그림에서 원점을
지나는 빨간색과 파란색의
두 직선을
가지고 설명합니다.
We're going to use two perpendicular lines - red and blue straight lines as shown below.
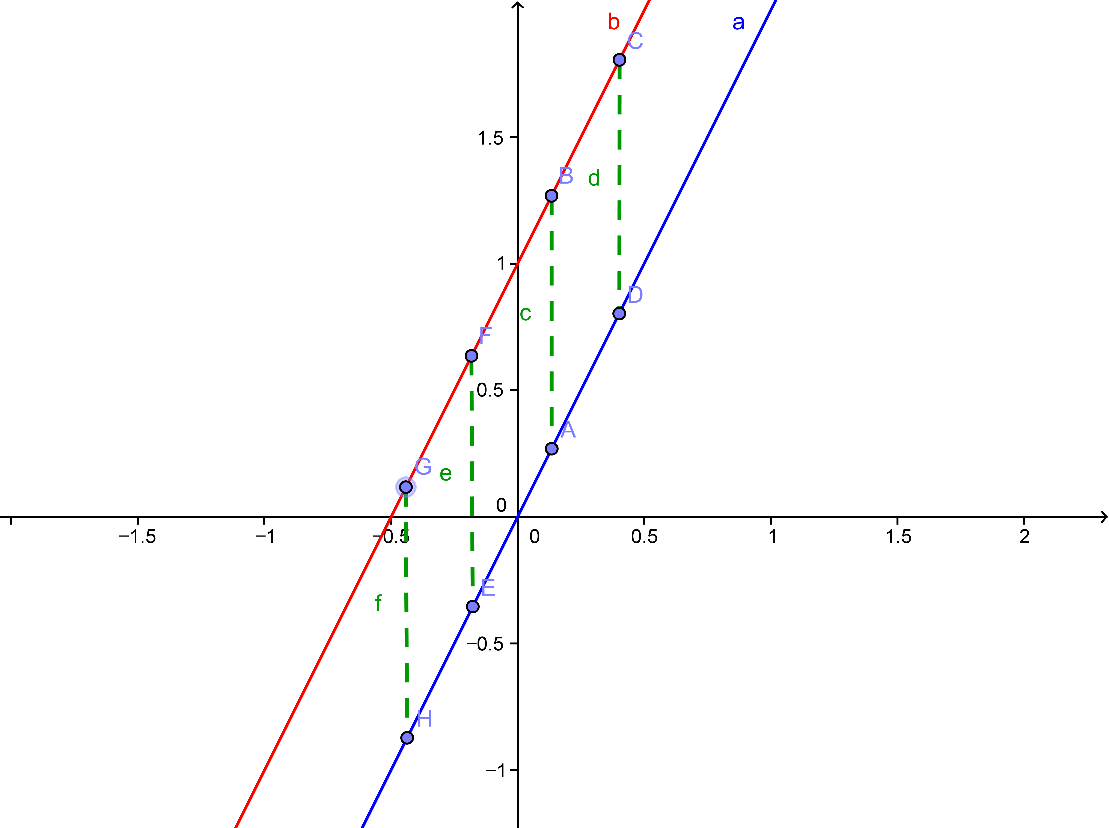
(1)
아래의 그래프와 같이
파란 직선 위의
한 점
B 를
잡고 이 점에서
x 축으로
수선을 내려 수선의
발을 A 라 합니다.
Draw a perpendicular line connecting the point A on x-axis
from the point B lying on the blue line in the figure shown below.
(2)
이번에는, 빨간색 직선
위에 OB = OE 가 되도록 점
E 를
잡습니다. 또, 점
E 에서
y 축으로
수선을 내려 수선의
발을 D 라고 합니다.
Next, find point E so that OB = OE on the red
line and draw a perpendicular line connecting the point D on y-axis.
(3)
위 그림에서
보이는, 파란색과 빨간색의
두 직각삼각형
ΔOAB 와
ΔODE 는
서로 합동 즉, 기호로는 ΔOAB ≡ ΔODE 입니다. 왜냐하면, 아래와 같이 직각삼각형의
[RHA] 합동조건 혹은
삼각형의 [AAS] 합동조건이
성립하기 때문입니다.
Right triangle ΔOAB shaded in blue and a red shaded right
triangle ΔODE are congruent (ΔOAB ≡ ΔODE) by [RHA] or
[AAS] rules.
(a)
수선을 내렸으니까, ∠A = ∠D = ∠R = 90˚
☞ Right angle (or Angle)
(b)
처음부터 길이가 같도록
잡았으니까, OB = OE
☞ Hypotenuse (or Side)
(c)
또, ∠EOD +∠DOB = ∠DOB + ∠BOA = ∠R = 90˚ 이므로, ∠EOD = ∠BOA
☞ Angle
참고로 우리나라에서는 직각삼각형의
[RHA] 합동조건을 사용하고
있지만, 대부분의 영어권
국가에서는 삼각형의 [AAS] 합동조건의 방법으로
가르치고 있습니다.
For
your reference, Korean teachers prefer [RHA] to [AAS] when they teach right triangle congruence.
(4) 두 직각 삼각형은 서로 합동이니까, AB = DE 이고 OA = OD 가 됩니다.
Congruent triangles have same legs, that is, AB = DE and
OA = OD.
(5) 여기서, 파란색 직선의 기울기는 AB ÷ OA 이고, 파란색 직선의 기울기는 DE ÷ (– OD) 이므로, 두 직선의 기울기를 서로 곱하면 – 1 이 됩니다.
The slope of blue line is (AB ÷ OA) whereas red line
has the slope of {OD ÷ (–DE)}. Hence, the product of two slopes = – 1 as follows :
(AB
÷ OA) x {OD ÷ (–DE)}
= (AB
÷ OA) x {OA ÷ (–AB)}
= – 1
[ B ] 해석 기하 (coordinate geometry) 의 방법
직선을 평행 이동시켜도 그 기울기는 변하지 않으니까, 앞에서와 같이, 원점을 지나는 빨간색과 파란색의 두 직선을 가지고 설명합니다.
In the same way, we're using two perpendicular lines that pass through the origin
(0, 0) because shifted line keeps the same slope of an original one.
해석기하에서는 상대적으로 계산이 복잡해지기 때문에, 일반성을 훼손하지 않는 범위내에서 최소의 미지수를 사용해야 좋습니다.
It is important to use minimum number of unknown variables in
order to prevent unnecessary complicated calculations.
(1) 아래 그림에서 파란색 직선의 기울기를 k, 빨간 직선의 기울기를 m 이라 정하고, x 축 위에 두 점 C = (a, 0) 와 D = (b,
0) 를 잡습니다.
Let's suppose the slopes of blue and red lines are k and m
respectively and assume that point C
= (a, 0) and D = (b, 0) as shown below.
(2) 그리고, 두 점 C, D 에서 검은색 점선으로 표시된 수선을 올려서, 만나는 파란 직선 위의 점을 A 그리고 빨간색 직선 위에 점을 B 라고 하면,
Connect AC and BD to be perpendicular to x-axis as black
dotted segments shown above.
(3) 직선 위에 있는 점들은 직선식을 만족해야 하니까, 문자로 된 기울기의 값을 적용하면, A = (a, ka) 그리고 B = (b, mb) 라고 놓을 수 있겠지요?
Therefore, the coordinates are A = (a, ka) and
B = (b, mb) because y-coordinate value = (slope) x
(x-coordinate value).
문자로 정하는 것이니까, x 좌표나 기울기의 부호 (+/–) 와 전혀 상관이 없다는 점에 유의하세요.
The signs (+/–) of x-coordinate and slope do not matter in this procedure because we are using
general term, i.e., letters.
(4) 각 점들의 좌표를 대입하여, 직각삼각형 세변의 길이를 구하면,
Find three side lengths in terms of coordinate values.
OA2 = a2 + (ka)2
OB2 = b2 + (mb)2
AB2 = (ka – mb)2
(4) 이제, 위 그림에서 보라색의 칠해진 ΔOAB 를 보면 직각삼각형이니까, [피타고라스의 정리] 를 적용하면,
Now, we can apply 'Pythagorean Theorem' to the purple shaded right
triangle as shown above.
a2 + (ka)2 + b2
+ (mb)2 = (a – b)2 + (ka – mb)2
0
= – 2ab – 2kamb
0 = – 2ab (1 + km)
(5) 그런데, 위 식에서 a 도 b 도 0 이 아니니까, km = – 1. 즉, 두 기울기의 곱은 – 1.
After simplification, neither a nor b is zero in the equation shown
above. Accordingly, 1 + km = 0, that is, the product of two slopes km = – 1.


Comments
Post a Comment